
Understanding your network to optimise maintenance
With Aigle 3D, Cerema is helping asset managers gain a better understanding of their networks, and optimise use of their maintenance budgets.
To take this approach even further, Cerema has developed a new vision of asset management that takes how networks are being adapted to the challenges of the future into account: climate change, new mobility, new technologies... and more.
Every year, €10bn are allocated to maintenance of roadway assets. In 1993, in an effort to support optimisation of maintenance schedules, the French government rolled out the IQRN indicator (Quality National Network Image), created by Cerema to assess levels of degradation on national highways, based on surveying the entire road network every year [1].
Aigle 3D was designed to accommodate this growing need for road condition diagnostics. In 2015, the French government asked Cerema to improve the IQRN indicator, by including the condition of all minor roads on an annual basis, and also surveying side roads every four years: Cerema rose to the challenge, and fitted next-gen 3D sensors to the vehicle.
Equipped in this way, Aigle 3D can provide high resolution 3D surveying of highway surfaces, and process the data to facilitate the scheduling of maintenance work, thanks to a cutting edge data processing system.
A vehicle equipped with completely new technology

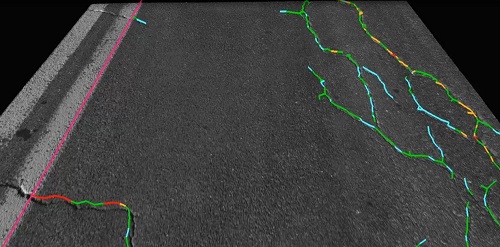
Aigle 3D creates a digital 3D image of the road surface, with one pixel per millimetre and a relative accuracy on the z-axis of 0.25mm. It can be used day or night, and at speeds of up to 130 km/h, on any road surface, and even in tunnels.
The technology can:
-
Automatically measure road geometry (incline, crossfall, curvature)
-
Automatically detect wear and signs of fatigue on different kinds of carriageway: cracks (longitudinal, lateral, check cracking), potholes, macrotextures, chunks, ravelling, rutting, changes to evenness (longitudinal, lateral).
-
Detect horizontal road markings
The vehicle is equipped with innovative tools:
-
Laser Crack Measurement System (LCMS) sensors developed by Pavemetrics in Quebec, fitted to bespoke vehicles specially made by Renault Tech to Cerema’s specifications in Cerema’s research and prototype centres.
-
The Toolholder Architecture (APO), developed by Cerema, used to control all of the vehicle’s measuring instruments.
-
A high-end Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) receiver, accompanied by a geographical data post-processing system that can accurately describe the location of any measurement taken with the device.
-
Remote maintenance and measurements so that diagnostics and actions can be carried out remotely, for more robust and reliable measurements.
Data processed at the Cerema server centre
The data collected by Cerema’s Aigle 3D vehicles are transferred to Cerema’s dedicated server centre where the following processing takes place:
-
Data processing using algorithms to detect damage, strain, signs of carriageway fatigue, and any objects on the carriageway (horizontal markings, drain holes, etc.). These algorithms were developed jointly by Pavemetrics and Cerema.
-
The precise GPS location of the data collected, to compile the geographical location database.
-
The processing, analysis, and study of the geographical data obtained, using Esri’s ArcGIS solution for reliable database compilation and use. These solutions can be used to compile relevant information, indicators, and tools, giving infrastructure managers the resources they need to make sound network management decisions.
-
Sharing and sending results to other databases (the infrastructure manager’s in particular). The tools used guarantee data interoperability (ArcGIS/Esri).
-
A unique server centre to collect and process data.
Cerema, the infrastructure expert, processes, interprets, and analyses the data to produce recommendations for scheduling road maintenance.
Furthermore, Cerema could position itself as the provider of a platform (the server centre) for analysing data collected by Aigle 3D, enabling it to aggregate data from different local authorities and organisations, thereby compiling an extremely accurate database of the conditions of French roads.
AIgle 3D will be unveiled at the Journées Techniques Route, Thursday 7 February, in a session dedicated to carriageway surveys and diagnostics.
De la route physique à son jumeau numérique
L’Aigle3D offre des performances remarquables :
- Large spectre de caractérisation de la chaussée, jusqu’au modèle 3D.
- Adaptation automatique aux limites de voie, gage de robustesse.
- Reproductibilité optimale des résultats.
- Précision géographique élevée.

